Cold Cooking Methods⁚ A Comprehensive Overview
This guide explores various cold cooking techniques, emphasizing their advantages in preserving flavors and nutrients․ We detail specific step-by-step methods, including ingredient selection, processes, and storage recommendations․ Comparisons with traditional cooking methods highlight benefits and limitations, aiding your culinary choices․
Introduction to Cold Cooking Techniques
Cold cooking, unlike traditional methods, avoids direct heat application․ This encompasses various techniques where ingredients are combined and allowed to meld flavors and textures at ambient or refrigerated temperatures․ Examples include marinating, curing, and cold-brewing․ These methods often involve extended timeframes, enabling gradual flavor infusion and enzymatic reactions to enhance the final product․ A key advantage is the retention of heat-sensitive nutrients and volatile aromatic compounds, resulting in dishes with enhanced flavor profiles and superior nutritional value․ Precise instructions, often found in detailed step-by-step PDFs, are crucial for successful cold cooking․
Benefits of Cold Cooking⁚ Flavor and Nutrient Retention
Cold cooking methods offer significant advantages in preserving both the flavor and nutritional integrity of ingredients․ Unlike high-heat cooking, which can degrade delicate compounds responsible for taste and aroma, cold preparation allows for a gradual extraction and blending of flavors․ This results in a more nuanced and complex taste profile․ Furthermore, heat-sensitive vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants are better retained in cold-cooked dishes․ The absence of high temperatures prevents the breakdown of these essential nutrients, leading to a healthier and more nutritious meal․ This is particularly beneficial for delicate fruits, vegetables, and proteins, which retain their vibrant colors and textures when prepared using cold methods․ Detailed step-by-step guides often highlight these benefits, emphasizing the importance of proper technique․
Cold Cooking Applications⁚ Examples and Recipes
Cold cooking encompasses a surprisingly wide range of culinary applications․ Popular examples include cold brewing coffee, a method yielding a smoother, less acidic beverage than traditional hot brewing․ Marinades, often prepared hours or even overnight, utilize cold temperatures to gently infuse flavors into meats and vegetables․ Similarly, many cold sauces and dressings rely on the emulsification of ingredients at room temperature or lower, creating stable and flavorful combinations․ Numerous recipes showcase the versatility of cold cooking, from simple fruit salads highlighting natural sweetness and textures to complex layered dishes incorporating cured meats and cheeses․ Step-by-step guides often provide detailed instructions for preparing these diverse culinary creations, ensuring success even for novice cooks․ The possibilities extend far beyond these examples, making cold cooking a dynamic and rewarding approach to food preparation․
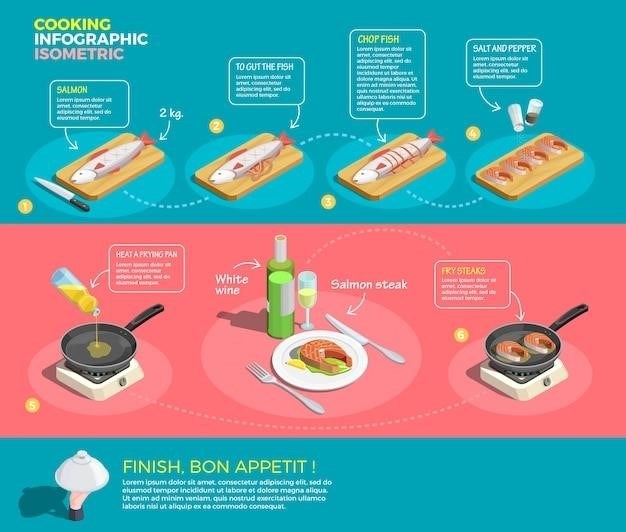
Step-by-Step Guide to a Specific Cold Cooking Method
This section provides a detailed, step-by-step guide to a particular cold cooking method, focusing on precise instructions and helpful tips to ensure successful results․ The guide will include comprehensive instructions and helpful illustrations․
Preparation and Ingredient Selection
Meticulous preparation is crucial for successful cold cooking․ Begin by assembling all necessary ingredients, ensuring they are fresh and of high quality․ For instance, if preparing a cold brew coffee, select freshly roasted beans, ideally coarsely ground․ For cold-cooked meats or salads, choose ingredients that will complement each other in terms of texture and flavor profiles․ Precise measurements are key; using a kitchen scale for dry ingredients enhances accuracy․ Thoroughly wash and sanitize all utensils and equipment that will come into contact with the food to prevent contamination․ Pre-chill ingredients like liquids to ensure even temperature distribution during the cold cooking process․ Proper preparation minimizes potential errors and maximizes the final product’s quality and taste․
The Cold Cooking Process⁚ Detailed Steps
The cold cooking process varies depending on the specific recipe․ For instance, cold brewing coffee involves steeping coarsely ground coffee in cold water for 12-24 hours․ This slow extraction method yields a smooth, less acidic brew․ In contrast, preparing a cold-smoked salmon requires a controlled environment with consistent temperature and airflow․ Precise timing is crucial; over-processing can result in undesirable textures or flavors․ For dishes involving marinades, ensure complete submersion of ingredients for even flavor penetration․ Regular monitoring of temperature and timing is essential, especially for large batches or complex preparations․ Detailed instructions, often found in step-by-step PDFs, are invaluable for achieving consistent results․ Adhering to these guidelines ensures a successful cold cooking experience․
Storage and Serving Recommendations
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of cold-cooked foods․ Cold-brewed coffee, for instance, should be refrigerated in an airtight container for up to two weeks․ Cold-smoked salmon benefits from vacuum sealing and freezing for longer preservation, while maintaining its delicate flavor profile․ For dishes involving marinades, ensure complete cooling before refrigeration to prevent bacterial growth․ Always use clean, sanitized containers to prevent cross-contamination․ Serving recommendations vary greatly depending on the dish․ Cold-brewed coffee can be served over ice, diluted with water or milk, or used as a base for cocktails․ Cold-smoked salmon is best enjoyed on its own or as part of a delicate appetizer․ Remember to always check internal temperatures before serving and adhere to safe food handling practices to ensure a pleasant and safe culinary experience․

Comparing Cold Cooking to Traditional Methods
Cold cooking methods offer unique advantages, preserving nutrients and delicate flavors often lost through heat․ However, they may require longer preparation times and specific storage considerations compared to traditional cooking․
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cold Cooking
Cold cooking presents several compelling advantages․ Firstly, it excels at preserving the delicate nuances of flavors and aromas, often lost in high-heat cooking methods․ Vitamins and other essential nutrients are also better retained, leading to healthier, more vibrant dishes․ The extended preparation time required can be seen as a disadvantage, as some recipes demand significant advance planning․ Moreover, cold cooking may not achieve the same textural changes as traditional methods; for instance, searing or browning aren’t possible without heat․ Successfully implementing cold cooking necessitates careful attention to food safety, particularly concerning temperature control and the potential for bacterial growth․ The lack of immediate gratification and the need for meticulous planning may deter some cooks․ However, the rewards of enhanced flavor and nutrient retention often outweigh these considerations, making cold cooking a valuable addition to any culinary repertoire․ Ultimately, the suitability of cold cooking depends on the specific recipe and the cook’s priorities and patience․
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Selecting the optimal cooking method hinges on several crucial factors․ Firstly, consider the desired outcome⁚ Do you prioritize preserving delicate flavors and nutrients, or achieving specific textural changes like browning or crispiness? Cold cooking shines when nutrient retention and subtle flavors are paramount, as seen in cold-brewed coffee or certain marinades․ However, if a browned crust or quickly seared exterior is needed, traditional heat-based methods are superior․ Secondly, evaluate your available time and resources․ Cold cooking often necessitates longer preparation times due to extended marinating or chilling periods․ Lastly, prioritize food safety․ Meticulous temperature control is essential to prevent bacterial growth when using cold cooking techniques․ By carefully weighing these factors—desired outcome, time constraints, and food safety—you can confidently choose the cooking method that best suits your needs and produces the desired culinary result․ Remember to always consult reputable sources for detailed instructions and safety guidelines;
